The Basics of Wooden Pallets
The pallet industry in the United States:
- 1.9 billion pallets are in use in the U.S. each year.
- Solid wood pallets make up 92% of the U.S. market.
- 441 million new wood pallets were manufactured in the U.S. in 2006.
- 321 million pallets were recovered/repaired/remanufactured in the U.S. in 2006.
Common Pallet Sizes in the U.S. (2011):
- 48" x 40" = 24.4%
- 42" x 42" = 4.8%
- 40" x 48" = 2.8%
- 48" x 36" = 1.5%
- 36" x 36" = 1.8%
- 48" x 48" = 3.8%
- 44" x 44" = 3.0%
- 800mm x 1200mm (Euro) = 0.7%
- Other (Custom) = 57.1%
Plastic Pallets:

Paperboard Pallets:

Wood Pallets:

Pallet design by entry method:
Two-way entry wood pallet:

Partial four-way entry wood pallet:

Four-way entry wood pallet:

Pallet design by base configuration:
Unidirectional base wood pallet:

Perimeter base wood pallet:

Cruciform base plastic pallet:

Solid Wood Pallets
79% of the U.S. market consists of solid wood pallets and 92% of pallet users use them
Advantages:
- Inexpensive
- Easy to prototype
- Strong
- Stiff
- Recyclable
- Can be designed using PDS
- Existing equipment and packaging is designed for the best performance using wood pallets.
Disadvantages:
- Fasteners
- Can harbor bugs
- Splintering
- Gaps between boards
- Give off moisture
- Variations between pallets
- Different lumber specs for different locations
Plastic Pallets
11% of the U.S. market consists of plastic pallets and 37% of pallet users use them.
Advantages:
- Bug free
- Durable
- Washable
- No fasteners
- Weather resistant
- Design potential
- Custom colors
Disadvantages:
- High purchase price
- Expensive to prototype
- Low friction
- Low stiffness
- Fire safety rating
- Not repairable
- Slower production times
Composite Pallets
18% of pallet users use composite pallets.
Advantages:
- Smooth deck
- Dry
- Bug free
- Good product protection
- Durable
- Design flexibility
- Can be designed using pallet design software
Disadvantages:
- High purchase price
- Expensive to repair
- Splintering
- Less recyclable
- Less water resistant
- Fasteners
Paper Pallets
11% of the U.S. market consists of paper pallets and 8% of pallet users use them.
Advantages:
- Lightweight
- Ergonomic
- Smooth deck surface
- Recyclable
- Lower freight cost
- Dry
- Bug free
Disadvantages:
- High purchase price
- Susceptible to moisture
- Poor performance with flexible loads
- Not durable
- Less product protection
Metal Pallets
0.8% of the U.S. market consists of metal pallets and 7% of pallet users use them.
Advantages:
- Strong and stiff
- Durable
- Recyclable
- Fire resistant
- Bug free
- Sanitary
- Dry
- No Fasteners
- Impervious to extreme temperatures
- Excellent product protection
Disadvantages:
- High purchase price
- Weight
- Sharp edges
- Low friction
- Susceptible to rusting
Fundemental pallet design parameters:
Strength
- Racking
- Static (floor stacks)
- Dynamic (fork tine movement)
Functionality
- Stiffness
- Durability
- Size
- Weight
COST!!!

Cost breakdown of packaging within a typical unit load...
$ 1.80 = Stretch wrap
$8-$9 = Pallet
$45 = Corrugated cases
$324 = HDPE 32oz bottles
$ 1.80 = Stretch wrap
$8-$9 = Pallet
$210 = 3.5 gallon plastic pails


Best practices for stiffer pallets:
- Always know the stiffness of your pallet design!
- Measure the increase in stress distribution before you make a decision.
- Consider the stiffness change of the pallet before modifying the support conditions.
- Stiffer is better!
When pallets aren't stiff enough, unit load failures can happen!

Best practices for more durable pallets:
- The life of the pallet is specified in number of trips.
- Expendable pallets need to last only 1 trip.
- Reusable pallets need to last more than 1 trip.
- Use butted double nominal 6" boards as lead-edge boards.
- Use hardwood boards for the lead-edge of a pallet.
- Use better fasteners.
- Protect the lead-edge blocks or stringers from impacts.
- Don't design pallets for more than 10 years.
- Don't design pallets for longer than you can retain ownership.
When pallets aren't durable enough, board failures can happen!

Technology used to improve pallet durability:
The below image shows a pallet protector attached to fork tines which helps to distributes the load on a larger area.
The below image shows a pallet protector attached to the front of the pallet reduces the severity of impacts on blocks, stringers, and lead-edge boards of the pallet.


Potential ways to improve durability:
- 5-6% increase in the number of fasteners used = 56% durability improvement in pallets.
- Butting lead-edge deckboards = 38% durability improvement in pallets.
- Split-inhibitors in lead-edge boards = 48% durability improvement in pallets.
- Use dense hardwood instead of medium density hardwoods = 38% durability improvement in pallets.
- Use dense hardwood instead of Douglas Fir = 165% durability improvement in pallets.
- Use air-dry pallets instead of green pallets = 43% durability improvement in pallets.
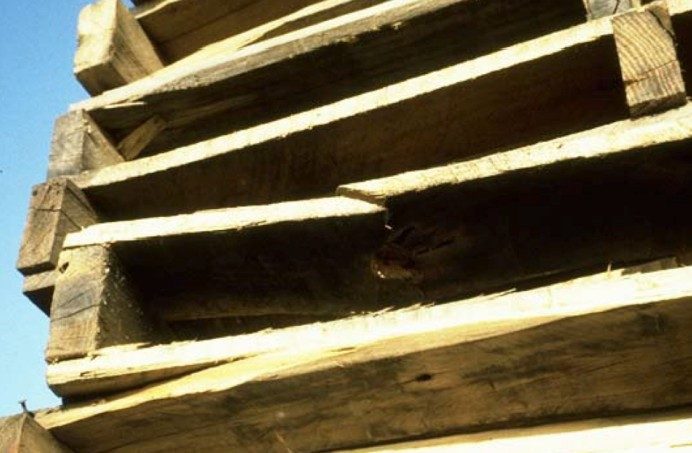
When pallets aren't durable enough, board splitting can happen!
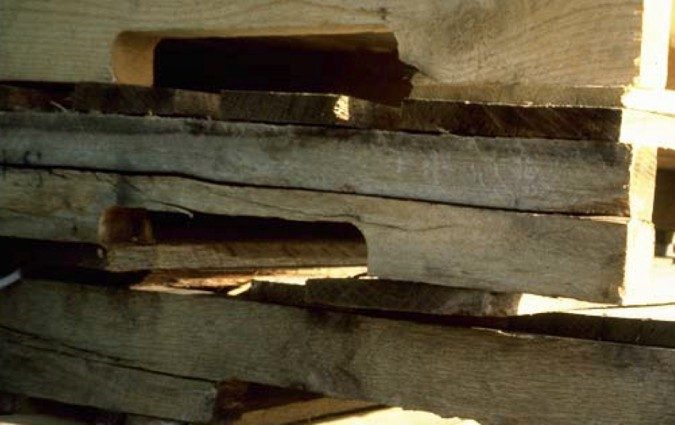

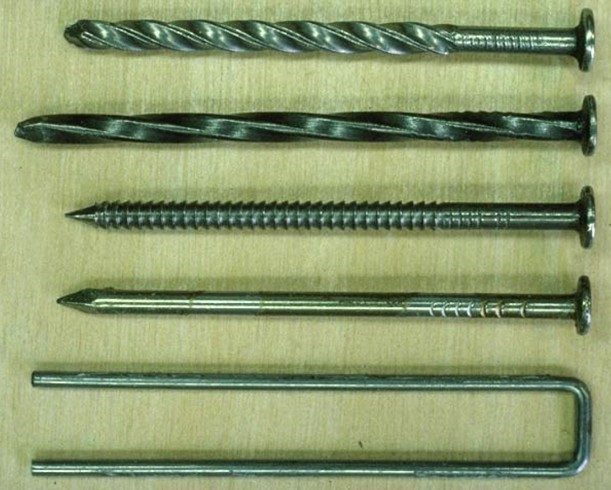
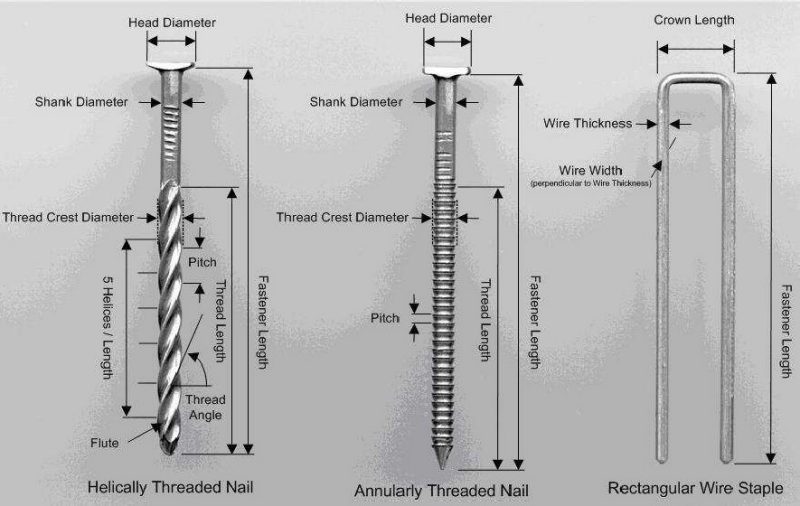
Basic pallet fasteners:
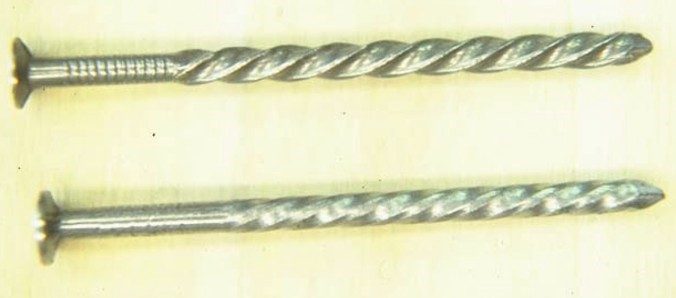
- Helically threaded nail
- Twisted square wire nail
- Annularly threaded nail
- Plain shank nail
- Round wire staple

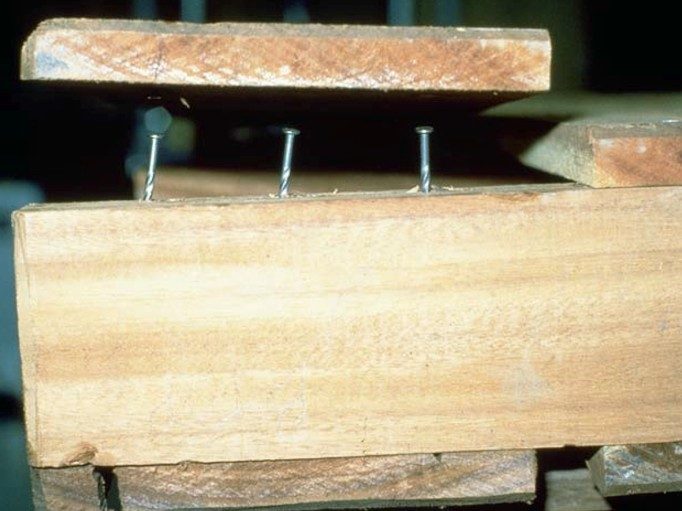
Issues caused by fasteners: Fastener Splitting

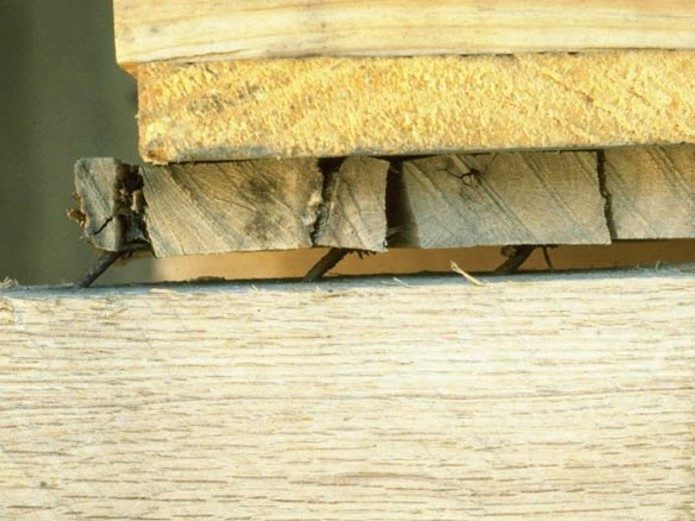
Issues caused by fasteners: Fastener Bending

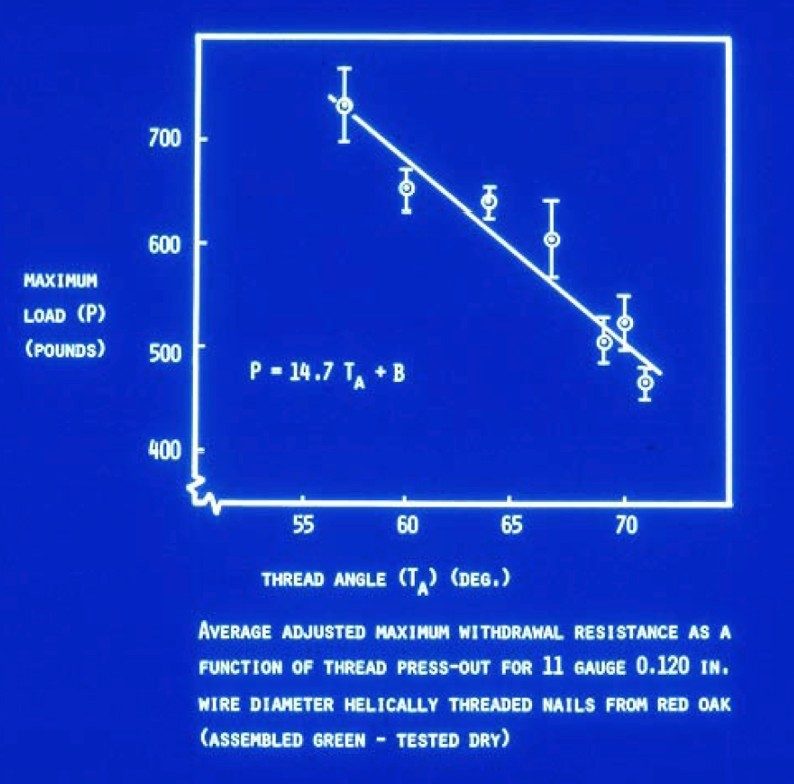
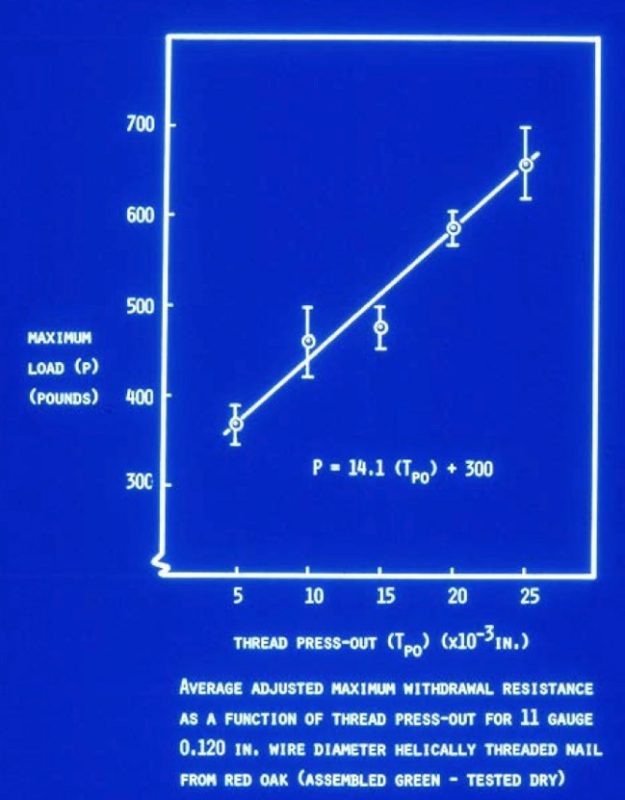
Effect of Thread Press-Out:
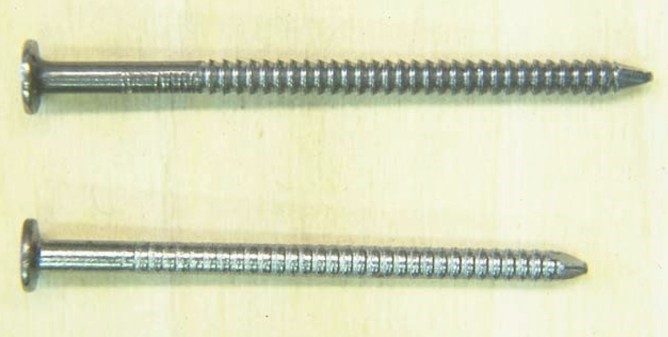
Effect of Helix Angle: